

Lesson 20: Malaria
anopheles
anticoagulant
anti-malarial
blood transfusion
coagulate
droplet
jaundice
malaria
mosquito
nourish
organ transplant
parasite
prophylaxis
protozoa
saliva
transmission
transmit
vaccine
catch a disease
Activity 1: Match the terms on the left with their meanings on the right.
|
1. nourish |
a) allow another person to reuse a needle you have used |
|
2. transmit |
b) replacing an organ from one body into another body |
|
3. parasite |
c) type of intravenous drip which gives blood to a person |
|
4. coagulate |
d) liquid found in the mouth which helps to make food softer |
|
5. organ transplant |
e) organism which feeds on another organism |
|
6. blood transfusion |
f) feed or give nutrients to something or someone |
|
7. saliva |
g) form blood clots |
|
8. share needles |
h) send from one area or person to another place or person |
Medical terms: anti - and ante-
These two prefixes can be confused.
anti - means ‘against’ or ‘counteracts’ e.g. anti-malarial = ‘against malaria’
ante- means ‘before’ e.g. antecedent = ‘something which goes before’
Picture on wikipedia by Jfbranch14 23 May 2012
What is malaria?
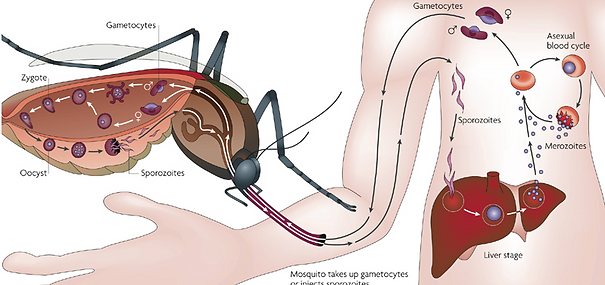
Malaria is a disease which is caused by a parasite found in the bite of infected anopheles mosquitoes.
The parasite that causes malaria is a protozoan parasite called Plasmodium. Protozoa are types of micro-organisms which only contain one cell. There are several plasmodium protozoa which can cause malaria. In Thailand, malaria is usually caused by Plasmodium falciparum or Plasmodium vivax.
People catch malaria when the parasite enters the blood when a female mosquito bites the person. Only the female mosquito sucks blood to use the blood to nourish her eggs. The Plasmodium protozoa is in the saliva of the mosquito. The mosquito also injects an anticoagulant to prevent the person’s blood from clotting.
Malaria is found in human blood so it can also be transmitted in the blood of blood transfusion, in organ transplantation and when sharing needles with infected blood. It cannot be transmitted from one person to another on the hands or by droplet transmission.
Activity 2: Answer the questions.
1. Malaria is caused by a ____________________ parasite.
a viral
b protozoan
c bacterial
2. The most common malarial parasites which cause malaria in Thailand are ______.
a p. falciparum and p.vivax
b p. falciparum and p. ovale
c p.vivax
3. It is only the female mosquito which _________________ the parasite.
a transfers
b transplants
c transmits
4. The mosquito ____________ the parasite and an anti-coagulant into the blood stream.
a injects
b infects
c sucks
5. Malaria is a disease which is _______________ in the blood or in blood products.
a passed through
b passed on
c passed in
Activity 3: Complete the information below.
What happens when an anopheles mosquito bites?
Before you start, review these terms
hepato- liver
- cyte cell
liver infect mosquito
dormant parasites bloodstream
An infected (1) ________________ bites into a person's skin to suck blood. Sporozoites or infective protozoa in the mosquito's saliva enter the (2) _________________ and move towards the liver.
The parasites infect hepatocytes in the (3) ____________ and multiply there for between 8 and 30 days.
After the (4) _______________ or ‘sleeping’ period in the liver, cells infected with sporozoites break open and release merozoites into the bloodstream.
Thousands of merozoites then (5) ____________ red blood cells.
Within the red blood cells, the malaria (6) ______________ continue to multiply and periodically
invade fresh red blood cells. There are several of these cycles.
Watch the video on Youtube at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=15Jc8J29v0U
Activity 4: Put the words in the order that you hear them. The first one is done for you.
leaflet
headache and feel generally unwell
mosquito net
sick and vomit
mosquito repellents
drug resistance
symptoms of malaria
high risk malaria area -1-
anti-malarial tablets
jaundice
Activity 5: Match the compound words you heard in the video. The first one is done for you.
Activity 6: Watch the video and complete the dialogue. A nurse gives advice on malaria prevention to a traveller at the Traveller Clinic. Record it for your homework.
Traveller: Hello, nurse. I am travelling to a high risk malaria area next month. Can you give me some advice about what to take?
Nurse: Sure. If you are travelling to a high risk area, it’s best to (1) _____________ yourself against mosquito bites.
Traveller: OK. I see. Should I take anti-malarial tablets before I go away?
Nurse: No. Prophylaxis is not recommended because there is a lot of (2) ___________ resistance.
Traveller: So, what should I do?
Nurse: It’s important to (3) ____________ under a mosquito net. This will protect you from mosquito bites when you sleep.
Traveller: OK.
Nurse: Always use mosquito repellents. You can buy (4) ______________ sprays which contain a chemical called DEET. Or else, ones which contain natural products.
Traveller: Right. So, I need to get a mosquito net to sleep under and some mosquito repellent. Is that right?
Nurse: Yes. And you should also understand the (5) ______________ of malaria. The symptoms usually start between 7 and 8 weeks after infection. Some types of malaria don’t show any symptoms for several months.
Traveller: Oh, really? What are the symptoms?
Nurse: You need to see a doctor straightaway if you have a (6) ____________ especially with chills. I mean if you have a high temperature but you feel very cold and you shake a lot. You may also have a headache and feel generally unwell. Some people may feel sick and vomit.
Traveller: OK. I’ll go to the doctor immediately if I feel unwell especially if I have a fever.
Nurse: In the later stages, malaria may cause jaundice. Your skin becomes (7) _______ and the whites of the eye also turn yellow. It’s a result of damage to the liver.
Traveller: That sounds terrible!
Nurse: Yes, it can be very serious. Fortunately, you should be all right if you get early (8) ________________. Remember to go to the doctor or to hospital if you notice the symptoms I mentioned. I have a leaflet here which you might find helpful.
Traveller: Thanks. It looks useful.
Activity 7: Make a poster for tourists about ‘Malaria in Thailand’. Include a map with the high risk malaria areas. Give advice on prevention. Explain the symptoms of malaria.